Linux commands: du
A quick guide to the `du` command, used to calculate the space usage of files and directories
The du command will calculate the size of a directory as a whole:
du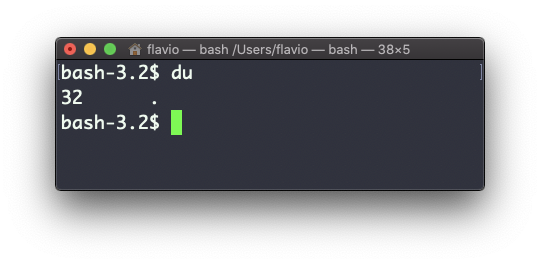
The 32 number here is a value expressed in bytes.
Running du * will calculate the size of each file individually:
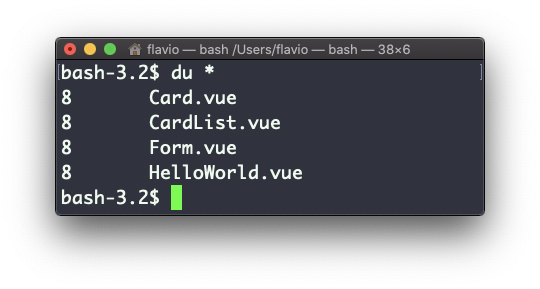
You can set du to display values in MegaBytes using du -m, and GigaBytes using du -g.
The -h option will show a human-readable notation for sizes, adapting to the size:
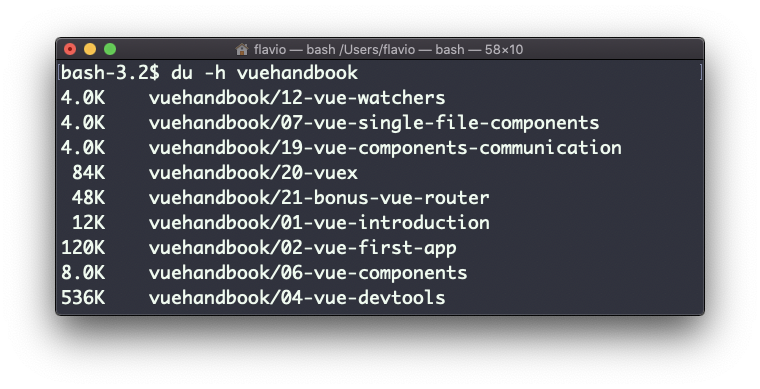
Adding the -a option will print the size of each file in the directories, too:
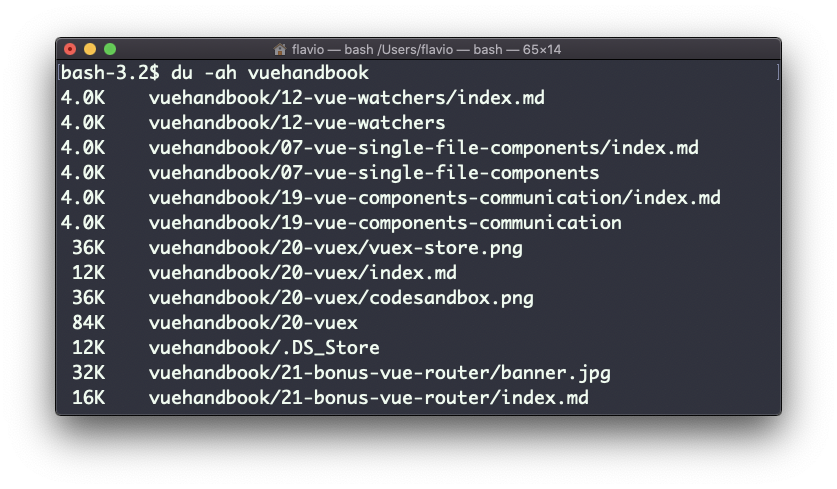
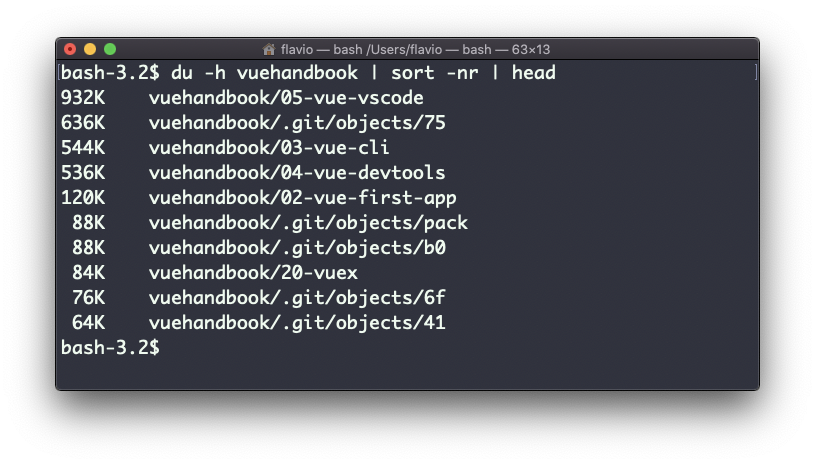
A handy thing is to sort the directories by size:
du -h <directory> | sort -nrand then piping to head to only get the first 10 results:
The
ducommand works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
download all my books for free
- javascript handbook
- typescript handbook
- css handbook
- node.js handbook
- astro handbook
- html handbook
- next.js pages router handbook
- alpine.js handbook
- htmx handbook
- react handbook
- sql handbook
- git cheat sheet
- laravel handbook
- express handbook
- swift handbook
- go handbook
- php handbook
- python handbook
- cli handbook
- c handbook
subscribe to my newsletter to get them
Terms: by subscribing to the newsletter you agree the following terms and conditions and privacy policy. The aim of the newsletter is to keep you up to date about new tutorials, new book releases or courses organized by Flavio. If you wish to unsubscribe from the newsletter, you can click the unsubscribe link that's present at the bottom of each email, anytime. I will not communicate/spread/publish or otherwise give away your address. Your email address is the only personal information collected, and it's only collected for the primary purpose of keeping you informed through the newsletter. It's stored in a secure server based in the EU. You can contact Flavio by emailing flavio@flaviocopes.com. These terms and conditions are governed by the laws in force in Italy and you unconditionally submit to the jurisdiction of the courts of Italy.