How to use Netcat
React Masterclass
Launching on November 4th
Netcat is a very useful Unix command we use to perform various networking tasks, and it’s very useful to debug and also learn how things work.
It’s available through the nc command.
Connect to any network server using this syntax:
nc DOMAIN PORT
nc localhost 8000
Once it’s connected to the server, you can send any message by typing them, and you will see any reply sent back by the server.
Like a simple 1-to-1 chat, upon which you can work on application-level functionality in the form of protocols (HTTP, FTP, SMTP, etc).
Using Netcat you can simulate all those application level protocols that power the Internet.
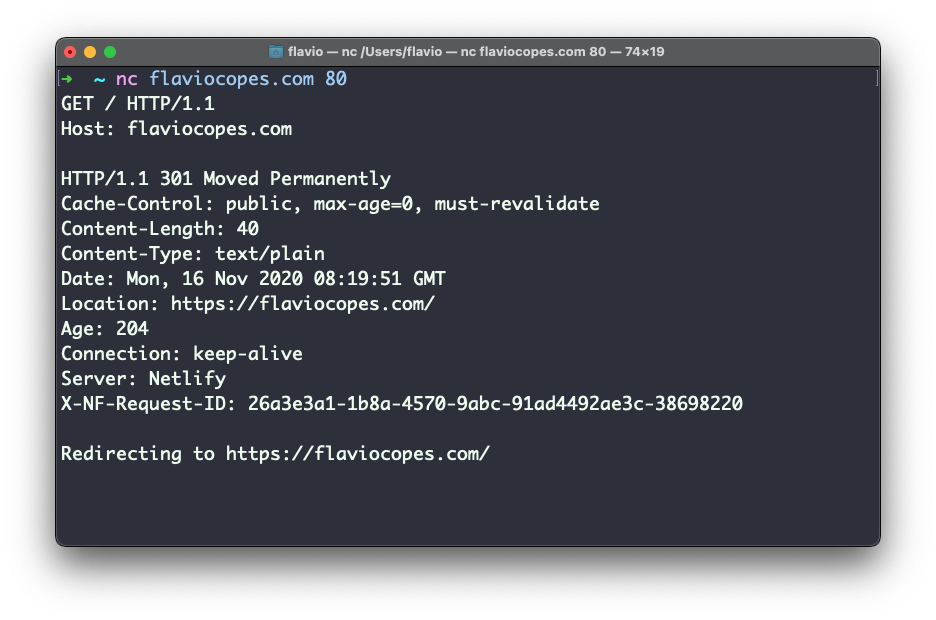
You can connect to a Web server and send it the HTTP protocol instructions. I can connect to my website with nc flaviocopes.com 80, and I can send it
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: flaviocopes.com
(the third line is an empty line)
and the server will reply back, with an HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently to https://flaviocopes.com/ response because I force HTTPS.
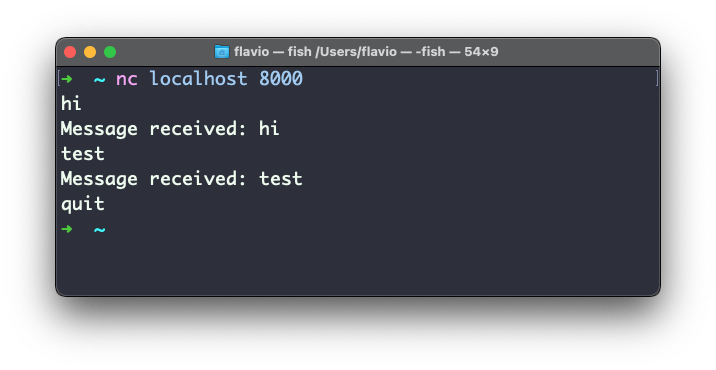
Here’s a simple example to interface with an “echo” server I built separately, that sends back what we send to it:
Netcat can work with TCP, the default protocol, or UDP.
To use UDP, add the -u flag:
nc -u localhost 8000
You can create a server, too. Use the -l (listen) option to listen on a specific port:
nc -l PORT
and Netcat will print every command received.
Try running the server with nc -l 8001 on one terminal window, and the client nc localhost 8001 on another, then send messages to the server by typing them in the client terminal.
Netcat can also be used for network inspection. You can scan the open ports of a server, in a specific range:
nc -v -z localhost 1-10000
Tip: combine with
grepto filter the noise:nc -v -z localhost 1-10000 2>&1 | grep succeeded
(if you’re curious which is the process using a port, run lsof -i :PORT)
You can tell a nc server to send the content of a file to the client that connects:
nc -l PORT < FILENAME
The client connecting with nc DOMAIN PORT will get the content of that file printed out, but it can save the content to a file using nc DOMAIN PORT > FILENAME, resulting in a basic file transfer.
After the file has been served, the server will terminate.
You can wrap that command in a simple Bash shell loop:
while true; do nc -l PORT < FILENAME; doneThat’s the simplest implementation of a Web server:
while true; do nc -l 80 < index.html; doneYou can tell the client to send to the server the instructions contained in a file:
nc DOMAIN PORT < FILENAME
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- JavaScript Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux/Mac CLI Commands Handbook
- C Handbook