Linux commands: uniq
A quick guide to the `uniq` command, used to work with duplicate records/lines in text
React Masterclass
Launching on November 4th
uniq is a command useful to sort lines of text.
You can get those lines from a file, or using pipes from the output of another command:
uniq dogs.txt
ls | uniqYou need to consider this key thing: uniq will only detect adjacent duplicate lines.
This implies that you will most likely use it along with sort:
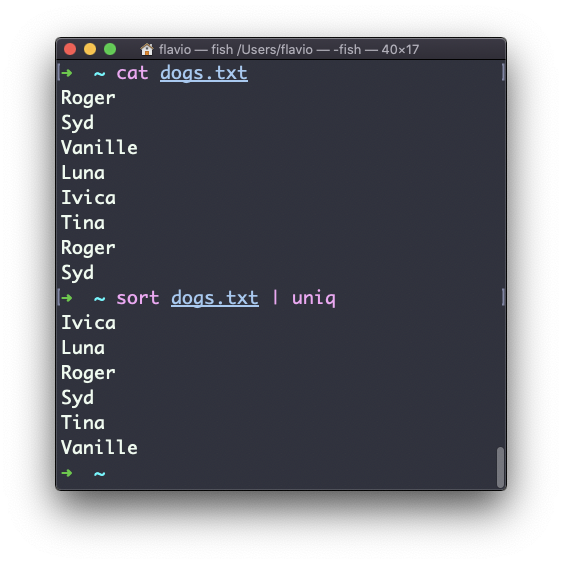
sort dogs.txt | uniqThe sort command has its own way to remove duplicates with the -u (unique) option. But uniq has more power.
By default it removes duplicate lines:
You can tell it to only display duplicate lines, for example, with the -d option:
sort dogs.txt | uniq -d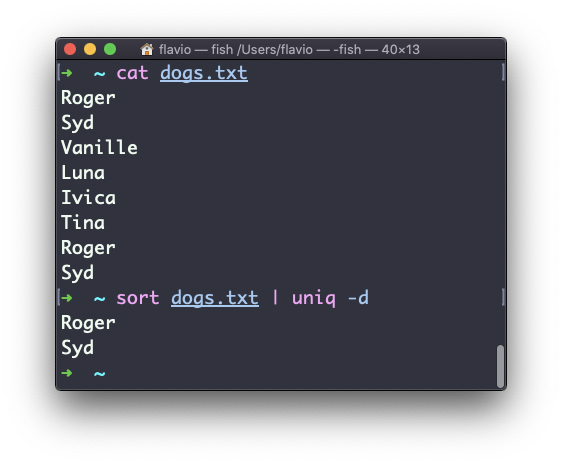
You can use the -u option to only display non-duplicate lines:
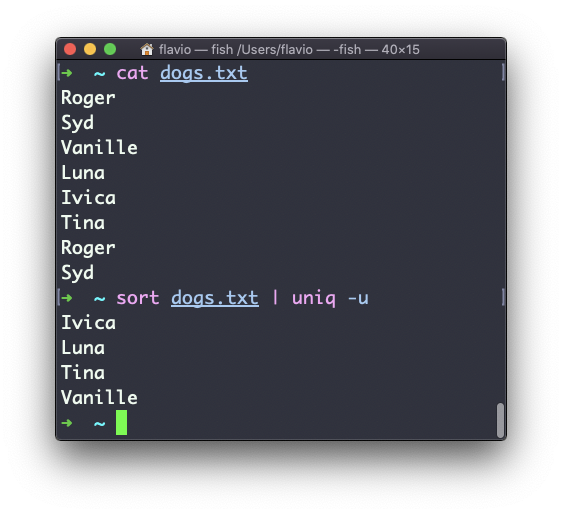
You can count the occurrences of each line with the -c option:
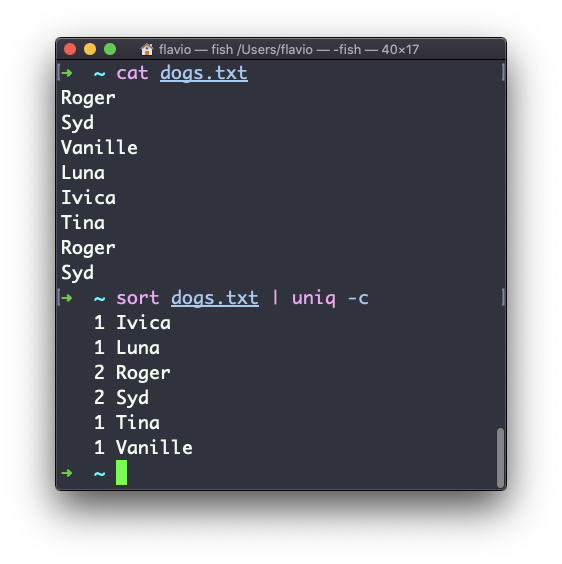
Use the special combination:
sort dogs.txt | uniq -c | sort -nrto then sort those lines by most frequent:
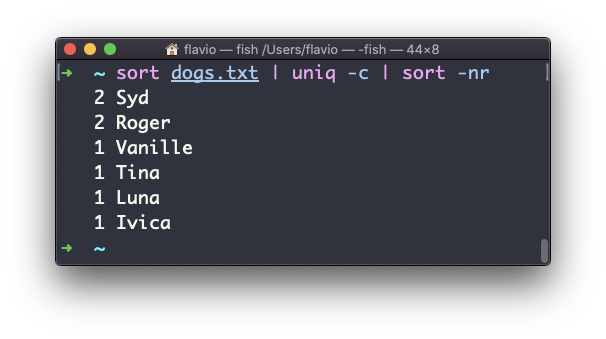
The uniq command works on Linux, macOS, WSL, and anywhere you have a UNIX environment
I wrote 20 books to help you become a better developer:
- JavaScript Handbook
- TypeScript Handbook
- CSS Handbook
- Node.js Handbook
- Astro Handbook
- HTML Handbook
- Next.js Pages Router Handbook
- Alpine.js Handbook
- HTMX Handbook
- React Handbook
- SQL Handbook
- Git Cheat Sheet
- Laravel Handbook
- Express Handbook
- Swift Handbook
- Go Handbook
- PHP Handbook
- Python Handbook
- Linux/Mac CLI Commands Handbook
- C Handbook