Using WebSockets with Node.js
WebSockets are an alternative to HTTP communication in Web Applications. They offer a long lived, bidirectional communication channel between client and server.
WebSockets are an alternative to HTTP communication in Web Applications.
They offer a long lived, bidirectional communication channel between client and server.
Once established, the channel is kept open, offering a very fast connection with low latency and overhead.
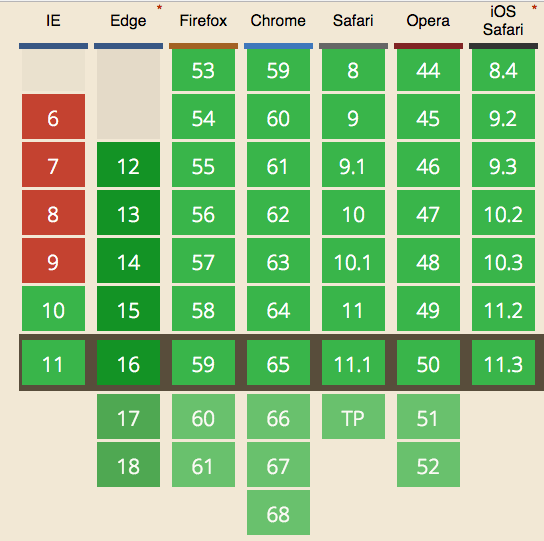
Browser support for WebSockets
WebSockets are supported by all modern browsers.
How WebSockets differ from HTTP
HTTP is a very different protocol, and also a different way of communicate.
HTTP is a request/response protocol: the server returns some data when the client requests it.
With WebSockets:
- the server can send a message to the client without the client explicitly requesting something
- the client and the server can talk to each other simultaneously
- very little data overhead needs to be exchanged to send messages. This means a low latency communication.
WebSockets are great for real-time and long-lived communications.
HTTP is great for occasional data exchange and interactions initiated by the client.
HTTP is much simpler to implement, while WebSockets require a bit more overhead.
Secured WebSockets
Always use the secure, encrypted protocol for WebSockets, wss://.
ws:// refers to the unsafe WebSockets version (the http:// of WebSockets), and should be avoided for obvious reasons.
Create a new WebSockets connection
const url = 'wss://myserver.com/something'
const connection = new WebSocket(url)connection is a WebSocket object.
When the connection is successfully established, the open event is fired.
Listen for it by assigning a callback function to the onopen property of the connection object:
connection.onopen = () => {
//...
}If there’s any error, the onerror function callback is fired:
connection.onerror = error => {
console.log(`WebSocket error: ${error}`)
}Sending data to the server using WebSockets
Once the connection is open, you can send data to the server.
You can do so conveniently inside the onopen callback function:
connection.onopen = () => {
connection.send('hey')
}Receiving data from the server using WebSockets
Listen with a callback function on onmessage, which is called when the message event is received:
connection.onmessage = e => {
console.log(e.data)
}Implement a WebSockets server in Node.js
ws is a popular WebSockets library for Node.js.
We’ll use it to build a WebSockets server. It can also be used to implement a client, and use WebSockets to communicate between two backend services.
Easily install it using
yarn init
yarn add wsThe code you need to write is very little:
const WebSocket = require('ws')
const wss = new WebSocket.Server({ port: 8080 })
wss.on('connection', ws => {
ws.on('message', message => {
console.log(`Received message => ${message}`)
})
ws.send('ho!')
})This code creates a new server on port 8080 (the default port for WebSockets), and adds a callback function when a connection is established, sending ho! to the client, and logging the messages it receives.
See a live example on Glitch
Here is a live example of a WebSockets server: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/flavio-websockets-server-example
Here is a WebSockets client that interacts with the server: https://glitch.com/edit/#!/flavio-websockets-client-example
download all my books for free
- javascript handbook
- typescript handbook
- css handbook
- node.js handbook
- astro handbook
- html handbook
- next.js pages router handbook
- alpine.js handbook
- htmx handbook
- react handbook
- sql handbook
- git cheat sheet
- laravel handbook
- express handbook
- swift handbook
- go handbook
- php handbook
- python handbook
- cli handbook
- c handbook
subscribe to my newsletter to get them
Terms: by subscribing to the newsletter you agree the following terms and conditions and privacy policy. The aim of the newsletter is to keep you up to date about new tutorials, new book releases or courses organized by Flavio. If you wish to unsubscribe from the newsletter, you can click the unsubscribe link that's present at the bottom of each email, anytime. I will not communicate/spread/publish or otherwise give away your address. Your email address is the only personal information collected, and it's only collected for the primary purpose of keeping you informed through the newsletter. It's stored in a secure server based in the EU. You can contact Flavio by emailing flavio@flaviocopes.com. These terms and conditions are governed by the laws in force in Italy and you unconditionally submit to the jurisdiction of the courts of Italy.