The Flexbox Tutorial
Flexbox, also called Flexible Box Module, is one of the two modern layouts systems, along with CSS Grid
Introduction
Flexbox, also called Flexible Box Module, is one of the two modern layouts systems, along with CSS Grid.
Compared to CSS Grid (which is bi-dimensional), flexbox is a one-dimensional layout model. It will control the layout based on a row or on a column, but not together at the same time.
The main goal of flexbox is to allow items to fill the whole space offered by their container, depending on some rules you set.
Unless you need to support old browsers like IE8 and IE9, Flexbox is the tool that lets you forget about using
- Table layouts
- Floats
- clearfix hacks
display: tablehacks
Let’s dive into flexbox and become a master of it in a very short time.
Enable Flexbox
A flexbox layout is applied to a container, by setting
display: flex;or
display: inline-flex;the content inside the container will be aligned using flexbox.
Container properties
Some flexbox properties apply to the container, which sets the general rules for its items. They are
flex-directionjustify-contentalign-itemsflex-wrapflex-flow
Align rows or columns
The first property we see, flex-direction, determines if the container should align its items as rows, or as columns:
flex-direction: rowplaces items as a row, in the text direction (left-to-right for western countries)flex-direction: row-reverseplaces items just likerowbut in the opposite directionflex-direction: columnplaces items in a column, ordering top to bottomflex-direction: column-reverseplaces items in a column, just likecolumnbut in the opposite direction
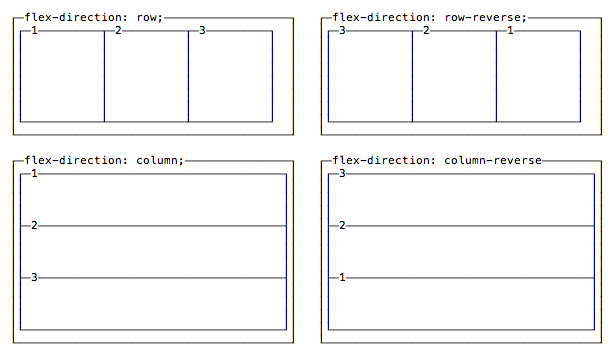
Vertical and horizontal alignment
By default items start from the left if flex-direction is row, and from the top if flex-direction is column.

You can change this behavior using justify-content to change the horizontal alignment, and align-items to change the vertical alignment.
Change the horizontal alignment
justify-content has 5 possible values:
flex-start: align to the left side of the container.flex-end: align to the right side of the container.center: align at the center of the container.space-between: display with equal spacing between them.space-around: display with equal spacing around them
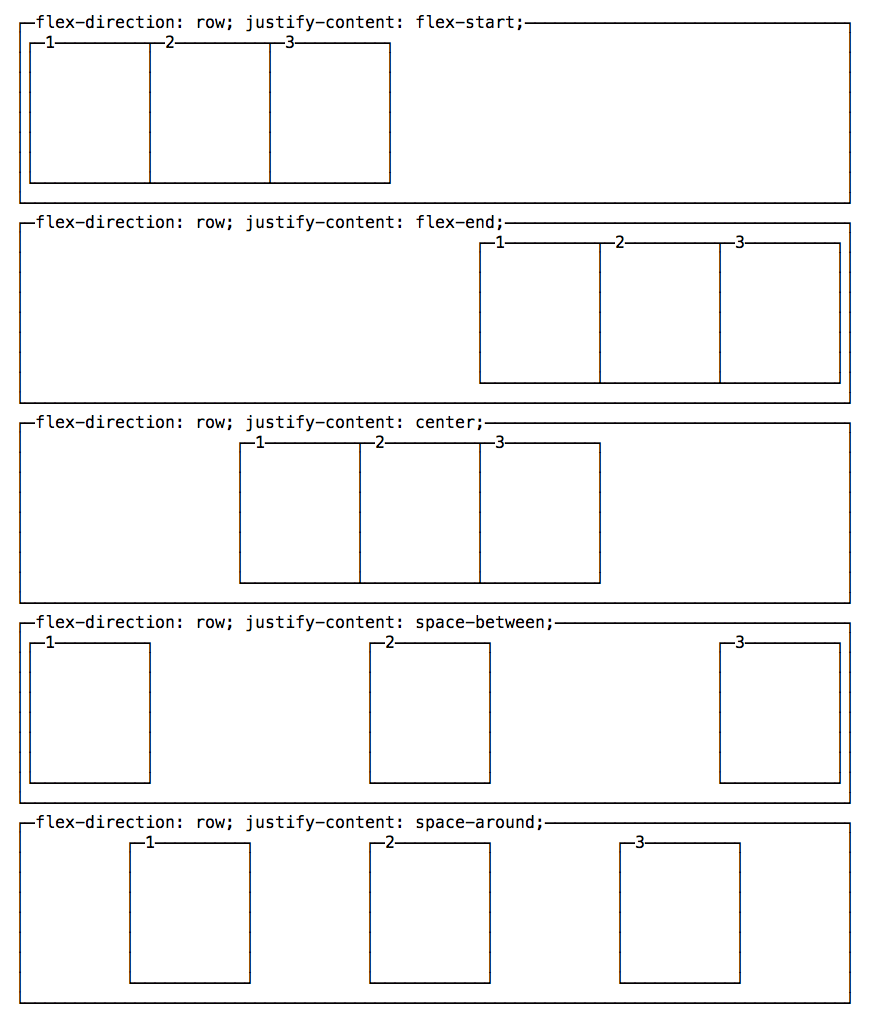
Change the vertical alignment
align-items has 5 possible values:
flex-start: align to the top of the container.flex-end: align to the bottom of the container.center: align at the vertical center of the container.baseline: display at the baseline of the container.stretch: items are stretched to fit the container.
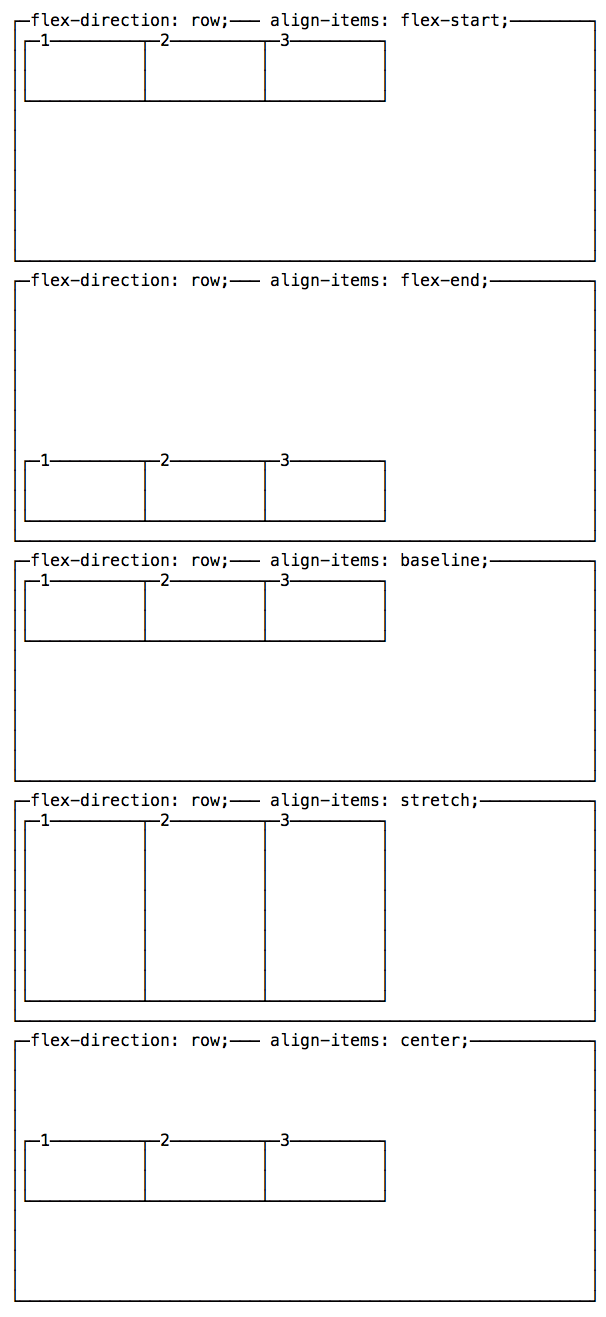
A note on baseline
baseline looks similar to flex-start in this example, due to my boxes being too simple. Check out this Codepen to have a more useful example, which I forked from a Pen originally created by Martin Michálek. As you can see there, items dimensions are aligned.
Wrap
By default items in a flexbox container are kept on a single line, shrinking them to fit in the container.
To force the items to spread across multiple lines, use flex-wrap: wrap. This will distribute the items according to the order set in flex-direction. Use flex-wrap: wrap-reverse to reverse this order.
A shorthand property called flex-flow allows you to specify flex-direction and flex-wrap in a single line, by adding the flex-direction value first, followed by flex-wrap value, for example: flex-flow: row wrap.
Properties that apply to each single item
Since now, we’ve seen the properties you can apply to the container.
Single items can have a certain amount of independence and flexibility, and you can alter their appearance using those properties:
orderalign-selfflex-growflex-shrinkflex-basisflex
Let’s see them in detail.
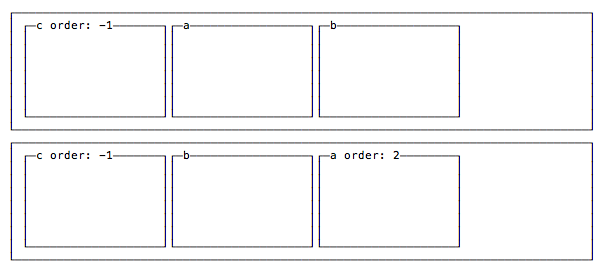
Moving items before / after another one using order
Items are ordered based on a order they are assigned. By default every item has order 0 and the appearance in the HTML determines the final order.
You can override this property using order on each separate item. This is a property you set on the item, not the container. You can make an item appear before all the others by setting a negative value.
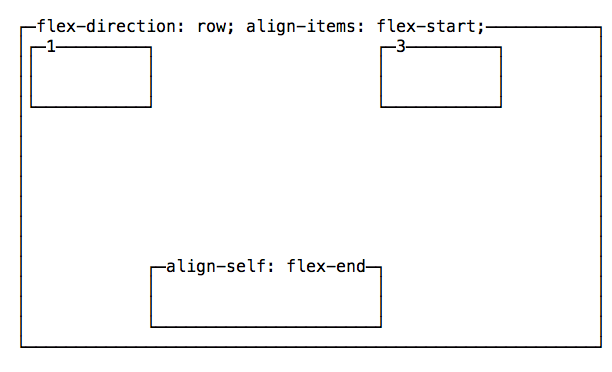
Vertical alignment using align-self
An item can choose to override the container align-items setting, using align-self, which has the same 5 possible values of align-items:
flex-start: align to the top of the container.flex-end: align to the bottom of the container.center: align at the vertical center of the container.baseline: display at the baseline of the container.stretch: items are stretched to fit the container.
Grow or shrink an item if necessary
flex-grow
The defaut for any item is 0.
If all items are defined as 1 and one is defined as 2, the bigger element will take the space of two “1” items.
flex-shrink
The defaut for any item is 1.
If all items are defined as 1 and one is defined as 3, the bigger element will shrink 3x the other ones. When less space is available, it will take 3x less space.
flex-basis
If set to auto, it sizes an item according to its width or height, and adds extra space based on the flex-grow property.
If set to 0, it does not add any extra space for the item when calculating the layout.
If you specify a pixel number value, it will use that as the length value (width or height depends if it’s a row or a column item)
flex
This property combines the above 3 properties:
flex-growflex-shrinkflex-basis
and provides a shorthand syntax: flex: 0 1 auto
download all my books for free
- javascript handbook
- typescript handbook
- css handbook
- node.js handbook
- astro handbook
- html handbook
- next.js pages router handbook
- alpine.js handbook
- htmx handbook
- react handbook
- sql handbook
- git cheat sheet
- laravel handbook
- express handbook
- swift handbook
- go handbook
- php handbook
- python handbook
- cli handbook
- c handbook
subscribe to my newsletter to get them
Terms: by subscribing to the newsletter you agree the following terms and conditions and privacy policy. The aim of the newsletter is to keep you up to date about new tutorials, new book releases or courses organized by Flavio. If you wish to unsubscribe from the newsletter, you can click the unsubscribe link that's present at the bottom of each email, anytime. I will not communicate/spread/publish or otherwise give away your address. Your email address is the only personal information collected, and it's only collected for the primary purpose of keeping you informed through the newsletter. It's stored in a secure server based in the EU. You can contact Flavio by emailing flavio@flaviocopes.com. These terms and conditions are governed by the laws in force in Italy and you unconditionally submit to the jurisdiction of the courts of Italy.